This Part is Short but it has two very Important questions which I encounter On almost every Interview, The way I Answer it maybe many people will not like it but who cares.😂😂
Ans:-
{Small and simple answer}
- Nmap works on Two layers Network (Layer 3) and Transport (Layer 4)
{If they ask for more In-depth answer}
- Nmap Use Network layer to send packets , and for detecting whether the host is Up or not.
- Transport Layer is used for SYN scan and also to detect which ports are open/closed.
- Sequence number detection also happens in Transport Layer which is used to detect the OS of the target.
Ans:- This question can vary either they can ask you to explain this in a telephonic interview or in an online written interview, So you need to manage accrodingly.
This is the Cycle I usually follow while doing Pentesting.
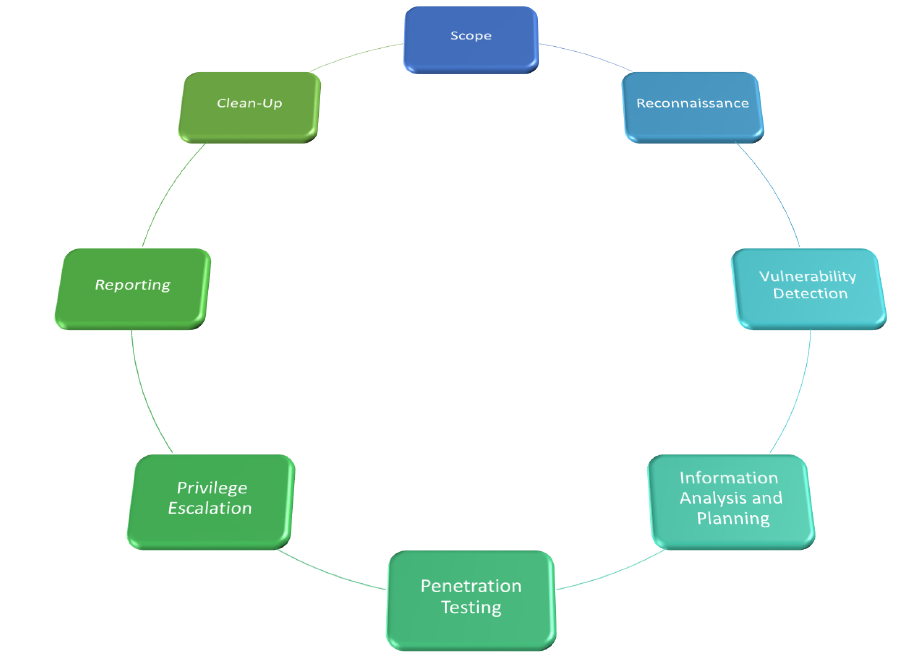
1) Scope - In this we need to find how many IP’s are available in the network, or provided by the client to scan.
2) Reconnaissance - this is the first interaction with the target machine in which we will enumerate to find the open ports for which we will use Nmap based on that result we will move to the next step.
Note: {The Target is given by the Client So I am not going to explain Passive Reconnaissance as it is simple to understand I guess you guys already know about it.}
3) Vulnerability Detection - Based on the Nmap result we need to find on which port the service is running and which version is installed.
4) Information Analysis and Planning – If we found any service which is running we will search for the public exploit if available or try to find it manually if it’s running any web server for which further enumeration of the web service we can use Nikto, gobuster, etc..
5) Penetration Testing - If the service we found is vulnerable to some sort of vulnerability
* For example, if there is old iweb http server is running then we can exploit it through directory traversal attack and download and have access to sensitive files.
Or if there is some service running like
* Achat 0.150 service running on port 9255 and 9256 then we can get a shell using a public bof exploit which is available on exploit db just by replacing the shell code we can get a shell.
6) Privilege Escalation – This is the most important part after gaining shell is to gain root access on the system, for that there are numerous ways, but first I like to go the old classic way by finding what permission the user have if we have user access, what is running on the crontab, what file permission we have and what are the binary file which have suid or guid permission on the server and on what kernel the server is running on, based on these enumeration we can try to privilege our user to get root level access.
7) Reporting – This is important step to create a clean and understandable report because sometime, the client we are interacting with is not that technically good, So we have to make a report in such a way so he can easily understand, and if possible there IT team can mimic the steps which we have done to compromise the machine by following the Report.
8) Clean-Up – This is the last and important part in which we need to clean the footprint before we go out, remove the logs of your system from the server, delete the file you download for enumeration or testing.
Twitter / Hack The Box / CTF Team / Teck_N00bs Community Telegram
Comments