This Post is all about Topics/Question which we had or could face in the Interview, This may not be the perfect but I tried to allign all the important Topic in this.
Speacial Thanx to my friend Ajay for hellping me find these question.
Ans:- Cross site request forgery (CSRF), also known as XSRF, Sea Surf or Session Riding, is an attack vector that tricks a web browser into executing an unwanted action in an application to which a user is logged in.
A successful CSRF attack can be devastating for both the business and user. It can result in damaged client relationships, unauthorized fund transfers, changed passwords and data theft—including stolen session cookies.
Ans:- The OWASP Top 10 is a powerful awareness document for web application security. It represents a broad consensus about the most critical security risks to web applications. Project members include a variety of security experts from around the world who have shared their expertise to produce this list.
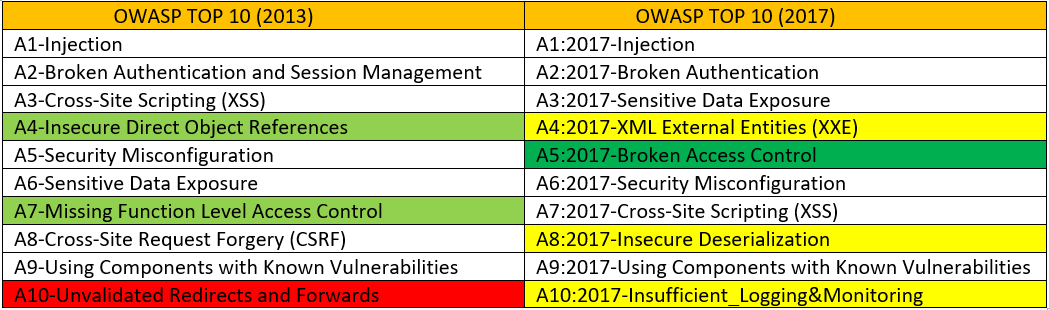
The current OWASP top ten list is (2017) version which includes :-
- A1:2017-Injection
- A2:2017-Broken Authentication
- A3:2017-Sensitive Data Exposure
- A4:2017-XML External Entities (XXE) [NEW]
- A5:2017-Broken Access Control [Merged]
- A6:2017-Security Misconfiguration
- A7:2017-Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- A8:2017-Insecure Deserialization [NEW, Community]
- A9:2017-Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
- A10:2017-Insufficient_Logging&Monitoring [NEW, Community]
Ans:-
- The Vulnerability A4 (Insecure Direct Object Reference) and A7 (Missing Function Level Access Control) in the 2013 list have been merged into single vulnerability A5 (Broken Access Control) of 2017.
- The vulnerability A10 (Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards) from 2013, has been dropped out in the new list of 2017.
- The Three new vulnerabilities which has been added in the new list are :-
- A4 (XML External Entities {XXE})
- A8 (Insecure Deserialization)
- A10 (Insufficient_Logging&Monitoring)
Ans:-
- Cross Site Flashing similar to Cross Site Scripting.
- Cross Site Flashing is an incredibly common vulnerability. It occurs due to the presence of flash content embedded inside a Web Application which tries to load flash content from another domain based on user’s input without any validation.
- Through this vulnerability the attacker may able to change the user interface of a web application to trick the user into providing his sensitive details.
- The attacker can leverage the fact that his flash content would run with similar privilege as that of the legitimate flash content on the vulnerable web application only if the application is vulnerable to cross site flashing.
- The attacker can also exploit to bypass access controls and perform harmful actions like stealing confidential data, installing malware, etc.
- This attack can also be used as an ‘enabler’ vulnerability to execute Cross-Site Scripting or Clickjacking attacks on the Web application.
Ans:- An XML External Entity attack is a type of attack against an application that parses XML input. This attack occurs when XML input containing a reference to an external entity is processed by a weakly configured XML parser. This attack may lead to the disclosure of confidential data, denial of service, server side request forgery, port scanning from the perspective of the machine where the parser is located, and other system impacts.
Ans:- Well SQL has a built in function to write a file for example:- in mysql using which You can save SQL results into an output of your choosing. So, lets say, 1 quote union select 2, and then we are going to type in a php string which we want to write into a file, using the output file mysql function, which we can then hopefully have the apache/php server execute for us. Lets just write this to /tmp/teck.php for now.
/blog.php?id=1' UNION select 2, "<?php system($_REQUEST['cmd']); ?>" INTO OUTFILE '/tmp/teck.php
As you can see down here, the mysql server happily executed our command. Lets just quickly take a look at the file. Okay, so what about if we had an uploads directory on our blog to allow users to upload pictures or something. Maybe we do not have the most secure permissions because we do not know any better. Lets create an uploads directory under /var/www/html/ and make it world writable. So, lets try and write our php file using the SQL injection vulnerability into /var/www/html/uploads/.
/blog.php?id=1' UNION select 2, "<?php system($_REQUEST['cmd']); ?>" INTO OUTFILE '/var/www/html/uploads/teck.php
Looks like it worked! Our SQL statement, took the php code we provided, and wrote it into a file. Lets head over to the uploads directory and have a look. Our files exists and works. Lets try and run a couple commands, like ls -l / for example, or what about the id command, as you can see we are running commands as the apache user now.
http://localhost:8080/uploads/c.php?cmd=ls -l /
Ans:-
- The Vulnerabilities in SSL Suites Weak Ciphers is prone to false positive reports by most vulnerability assessment solutions. AVDS is alone in using behavior based testing that eliminates this issue. For all other VA tools security consultants will recommend confirmation by direct observation.
- In any case Penetration testing procedures for discovery of Vulnerabilities in SSL Suites Weak Ciphers produces the highest discovery accuracy rate, but the infrequency of this expensive form of testing degrades its value.
- The ideal would be to have pen-testing accuracy and the frequency and scope possibilities of VA solutions, and this is accomplished only by AVDS.
Ans:- ‘ping’ uses ICMP, specifically ICMP echo request and ICMP echo reply packets. There is no ‘port’ associated with ICMP. Ports are associated with the two IP transport layer protocols, TCP and UDP. ICMP packets are identified by the ‘protocol’ field in the IP datagram header.
Ans:-
- Intrusion detection system evasion techniques are modifications made to attacks in order to prevent detection by an intrusion detection system (IDS).
- Almost all published evasion techniques modify network attacks. The 1998 paper Insertion, Evasion, and Denial of Service: Eluding Network Intrusion Detection popularized IDS evasion, and discussed both evasion techniques and areas where the correct interpretation was ambiguous depending on the targeted computer system.
- The ‘fragroute’ and ‘fragrouter’ programs implement evasion techniques discussed in the paper. Many web vulnerability scanners, such as ‘Nikto’, ‘whisker’ and ‘Sandcat’, also incorporate IDS evasion techniques.
- Most IDSs have been modified to detect or even reverse basic evasion techniques, but IDS evasion (and countering IDS evasion) are still active fields.
Ans:- HTTP headers allow the client and the server to pass additional information with the request or the response. A request header consists of its case-insensitive name followed by a colon ‘:’, then by its value (without line breaks). Leading white space before the value is ignored.
Headers can be grouped according to their contexts:-
- General header: Headers applying to both requests and responses but with no relation to the data eventually transmitted in the body.
- Request header: Headers containing more information about the resource to be fetched or about the client itself.
- Response header: Headers with additional information about the response, like its location or about the server itself (name and version etc.).
- Entity header: Headers containing more information about the body of the entity, like its content length or its MIME-type.
Ans:- There is often significant confusion around the differences between encryption, encoding, hashing, and obfuscation.
- Encoding :
- The purpose of encoding is to transform data so that it can be properly (and safely) consumed by a different type of system, e.g. binary data being sent over email, or viewing special characters on a web page. The goal is not to keep information secret, but rather to ensure that it’s able to be properly consumed.
- Encoding transforms data into another format using a scheme that is publicly available so that it can easily be reversed. It does not require a key as the only thing required to decode it is the algorithm that was used to encode it.
- Examples: ascii, unicode, url encoding, base64
- Encryption :
- The purpose of encryption is to transform data in order to keep it secret from others, e.g. sending someone a secret letter that only they should be able to read, or securely sending a password over the Internet. Rather than focusing on usability, the goal is to ensure the data cannot be consumed by anyone other than the intended recipient(s).
- Encryption transforms data into another format in such a way that only specific individual(s) can reverse the transformation. It uses a key, which is kept secret, in conjunction with the plaintext and the algorithm, in order to perform the encryption operation. As such, the cipher text, algorithm, and key are all required to return to the plaintext.
- Examples: aes, blowfish, rsa
- Hashing :
- Hashing serves the purpose of ensuring integrity, i.e. making it so that if something is changed you can know that it’s changed. Technically, hashing takes arbitrary input and produce a fixed-length string that has the following attributes:
- The same input will always produce the same output.
- Multiple disparate inputs should not produce the same output.
- It should not be possible to go from the output to the input.
- Any modification of a given input should result in drastic change to the hash.
- Hashing is used in conjunction with authentication to produce strong evidence that a given message has not been modified. This is accomplished by taking a given input, hashing it, and then signing the hash with the sender’s private key.
- When the recipient opens the message, they can then validate the signature of the hash with the sender’s public key and then hash the message themselves and compare it to the hash that was signed by the sender. If they match it is an unmodified message, sent by the correct person.
- Examples: sha-3, md5 (now obsolete), etc.
- Hashing serves the purpose of ensuring integrity, i.e. making it so that if something is changed you can know that it’s changed. Technically, hashing takes arbitrary input and produce a fixed-length string that has the following attributes:
- Obfuscation :
- The purpose of obfuscation is to make something harder to understand, usually for the purposes of making it more difficult to attack or to copy.
- One common use is the the obfuscation of source code so that it’s harder to replicate a given product if it is reverse engineered.
- It’s important to note that obfuscation is not a strong control (like properly employed encryption) but rather an obstacle. It, like encoding, can often be reversed by using the same technique that obfuscated it. Other times it is simply a manual process that takes time to work through.
- Another key thing to realize about obfuscation is that there is a limitation to how obscure the code can become, depending on the content being obscured. If you are obscuring computer code, for example, the limitation is that the result must still be consumable by the computer or else the application will cease to function.
- Examples: javascript obfuscator, proguard
Twitter / Hack The Box / CTF Team / Teck_N00bs Community Telegram
Comments